A new temperature record for the East Asian Summer Monsoon
Study unveils unprecedented insights into the climatic past of the East Asian Summer Monsoon
A new article, published in Science Advances, unveiled a comprehensive 21,000-year temperature record for north China, offering unprecedented insights into the climatic past of the East Asian Summer Monsoon. This monsoon system, vital for supplying freshwater to over a fifth of the world’s population, has long been a subject of intrigue. The collaboration between researchers, including several NESSC scientists, aims to address the gaps in our understanding.
The majority of insights into past climate changes have been derived from marine records, leaving terrestrial temperature records relatively unexplored. The scarcity of such records is attributed to the absence of suitable climate archives on land and the need for analytical tools capable of reconstructing absolute temperatures.

Innovative paleothermometers
To overcome these challenges, climate researchers applied two independent paleothermometers—clumped isotopes of snail shells and soil bacterial membrane lipids (brGDGTs)—to a loess-paleosol sequence from north China. This innovative approach allowed the reconstruction of a high-resolution temperature record spanning the past 21,000 years, with an average resolution of approximately 180 years.
Unravelling soil moisture’s role
A notable strength of the study lies in its validation process. The high-resolution record based on brGDGT distributions was compared with the clumped isotope composition of snail shells. Both records exhibited consistent trends and absolute temperatures, providing robust evidence of land surface growing season temperatures.
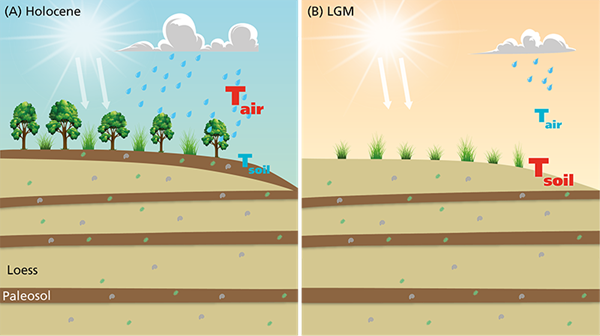
The researchers discovered a pivotal role played by soil moisture content in shaping land surface temperatures. Arid conditions during the last glacial maximum resulted in higher-than-expected temperatures, while the opposite mechanism led to lower-than-expected temperatures during the late Holocene. This principle was further confirmed using an energy partitioning model.
Future Considerations
The findings not only deepen our understanding of the temperature variability of the East Asian Monsoon area but also underscore the importance of considering soil moisture availability when comparing proxy records with climate model outputs. The emphasis on interdisciplinary collaboration and the utilization of diverse scientific tools pave the way for more accurate predictions and informed decision-making as we confront global climate challenges.
Article
Robust land surface temperature record for north China over the past 21,000 years
Jingjing Guo, Martin Ziegler, Niko Wanders et al.
Science Advances, 2024
https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adj4800

